
Notebooks are a web-based Jupyter IDE with shared persistent storage for long-term development and inter-notebook collaboration, backed by accelerated compute.
When you create a new Paperspace Notebook, you can either choose an existing template or create a custom notebook using advanced options.
In the Paperspace console, click the drop-down menu in the top-right corner, then click GRADIENT. In the Projects section, select the project you want to create a Jupyter notebook for. In the Notebooks tab of your project, click CREATE to go to the Launch a notebook page.
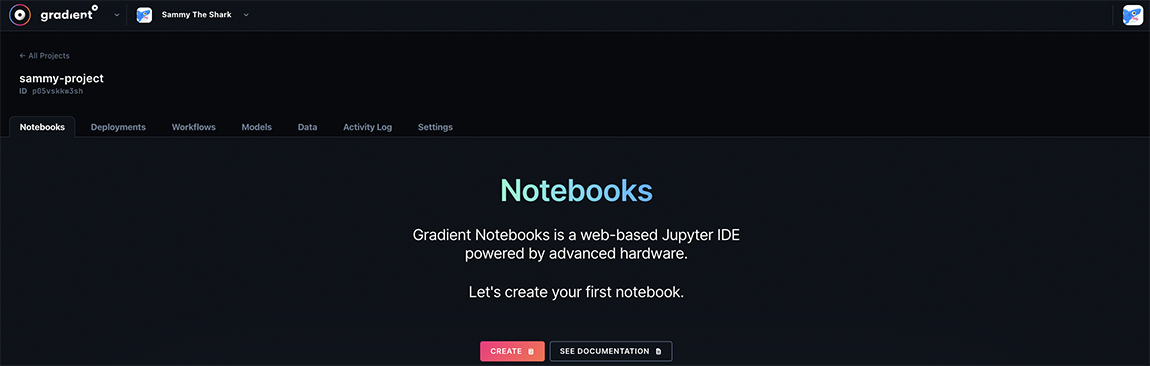
On Launch a notebook page, in the Select a template section, choose your desired template for your Jupyter environment.
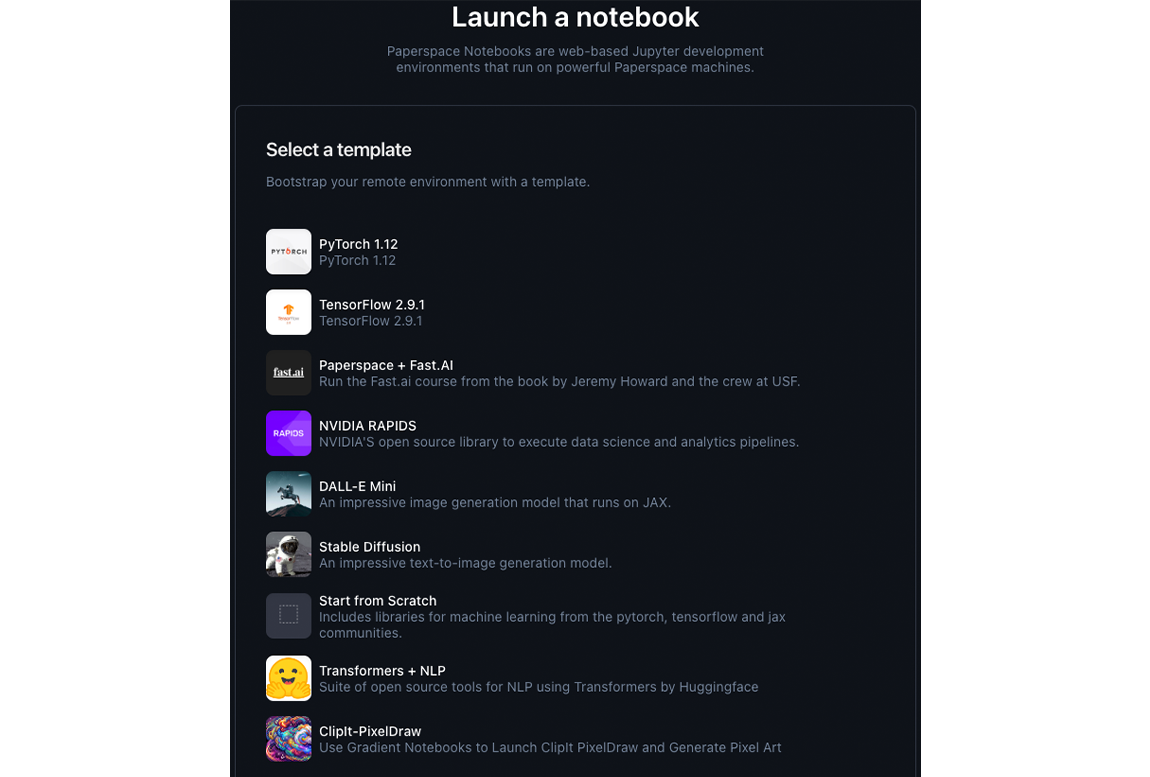
After selecting your template, the Select a machine section appears with a drop-down menu to select your machine type. Free compute is only available on personal accounts, and they have a max auto-shutdown limit of six hours. Finally, in the Auto-shutdown timeout section, select the amount of time your machine can idle before it shuts down.
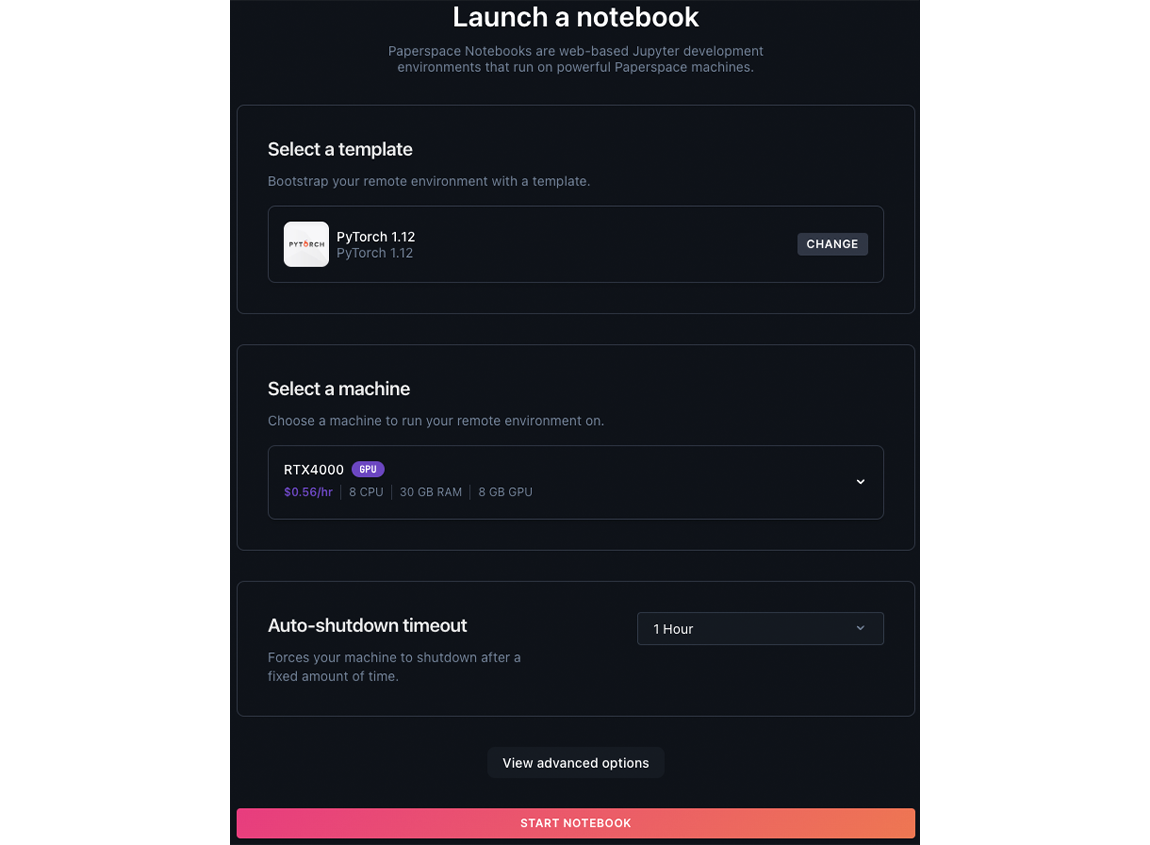
Optionally, at the bottom of the form, click the View advanced options button to further configure your notebook, like the notebook’s workspace and container. These options customize the remote environment’s container and workspace settings.
Under the Workspace section, you can customize the following attributes:
/notebooks directory.v1.1.1.Your Docker image is stored in a container registry, like Docker Hub or GitHub. Under the Container section, you can customize the following attributes for your Docker container:
registry/container-name:tag (for example, paperspace/Gradient-base:v1).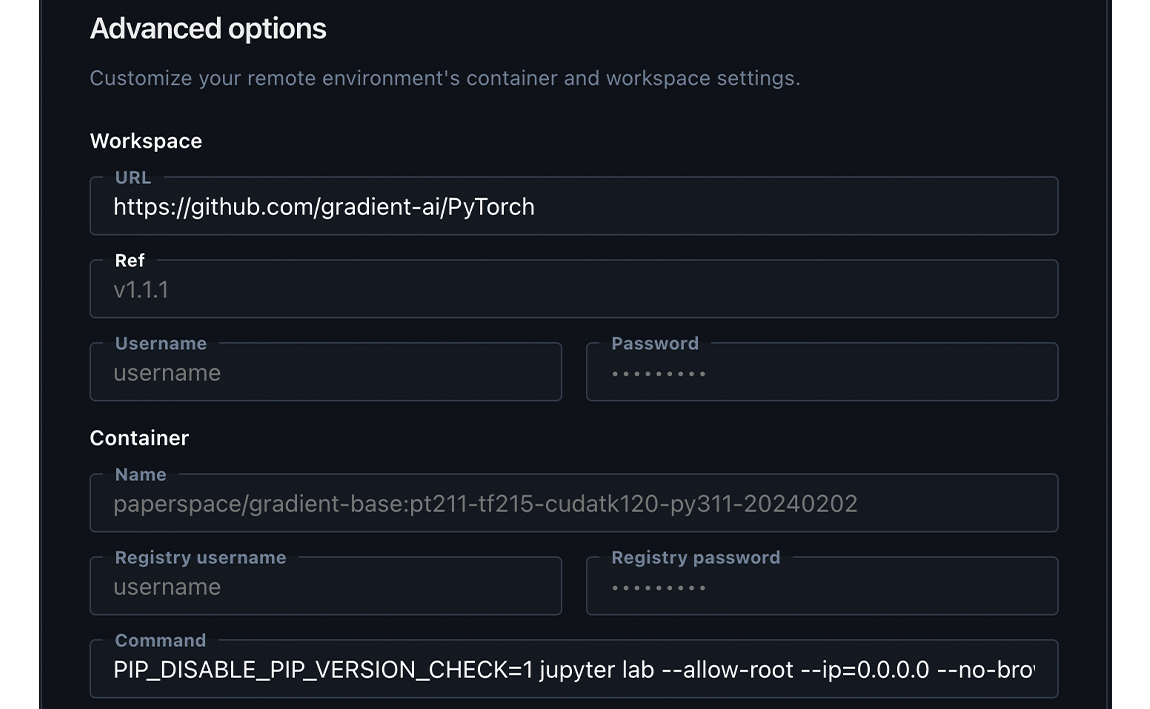
After you complete your notebook’s configuration, click START NOTEBOOK.